Buffalo Port Devices Driver
Notice
The Nintendo Wi-Fi USB Connector is a wireless game adapter, developed jointly by Nintendo and Buffalo Technology, which allows Nintendo DSi and Wii users without a Wi-Fi connection or compatible Wi-Fi network to establish one via a broadband-connected PC.Inserted into the host PC's USB port, the connector functions with the Nintendo DS, Wii, and DSi, permitting the user to connect to the.
For Windows version 1803 and later versions, if your platform supports the new Kernel DMA Protection feature, we recommend that you leverage that feature to mitigate Thunderbolt DMA attacks. For earlier versions of Windowsor platforms that lack the new Kernel DMA Protection feature, if your organization allows for TPM-only protectors or supports computers in sleep mode, the following is one DMA mitigation option. Please refer to BitLocker Countermeasures to understand the spectrum of mitigations.
- A complete list of available network device drivers for realtek rtl8168c/ this page, you will find all available drivers listed by release date for the windows 7 32bit operating system. Buffalo lgy-pci-gt gigabit lan card driver download - the western digital elements has rarely been this cheap.
- Download BUFFALO WLP-U2-433DHP Wireless Lan Adapter Wi-Fi device drivers or install DriverPack Solution software for driver update. BUFFALO WLP-U2-433DHP Wireless Lan Adapter Wi-Fi device drivers. Install drivers automatically. DriverPack software is absolutely free of charge. Available drivers.
- New: TeraStation 6000. With advanced snapshot feature and more. Read further NAS Systems read more Other Storage Solutions read more Network Components read more »Thanks to high performance and flexible access, we have grown globally while reducing costs, energy consumption and maintenance. « Mark Griffiths, IT Manager der Peers Hardy Group The company.

Also users may refer to Intel Thunderbolt 3 and Security on Microsoft Windows 10 Operating System documentation for alternative mitigations.
Microsoft provides third-party contact information to help you find technical support. This contact information may change without notice. Microsoft does not guarantee the accuracy of this third-party contact information.
For more information about how to do this, go to the following Microsoft website:
Symptoms
A BitLocker-protected computer may be vulnerable to Direct Memory Access (DMA) attacks when the computer is turned on or is in the Standby power state. This includes when the desktop is locked.
BitLocker with TPM-only authentication allows for a computer to enter the power-on state without any pre-boot authentication. Therefore, an attacker may be able to perform DMA attacks.
In these configurations, an attacker may be able to search for BitLocker encryption keys in system memory by spoofing the SBP-2 hardware ID by using an attacking device that is plugged into a 1394 port. Alternatively, an active Thunderbolt port also provides access to system memory to perform an attack. Note that Thunderbolt 3 on the new USB Type-C connector includes new security features which can be configured to protect against this type of attack without disabling the port.
This article applies to any of the following systems:
Systems that are left turned on
Systems that are left in the Standby power state
Systems that use the TPM-only BitLocker protector
Cause
1394 physical DMA
Industry standard 1394 controllers (OHCI compliant) provide functionality that allows for access to system memory. This functionality is provided as a performance improvement. It enables large amounts of data to transfer directly between a 1394 device and system memory, bypassing CPU and software. By default, 1394 Physical DMA is disabled in all versions of Windows. The following options are available to enable 1394 Physical DMA:
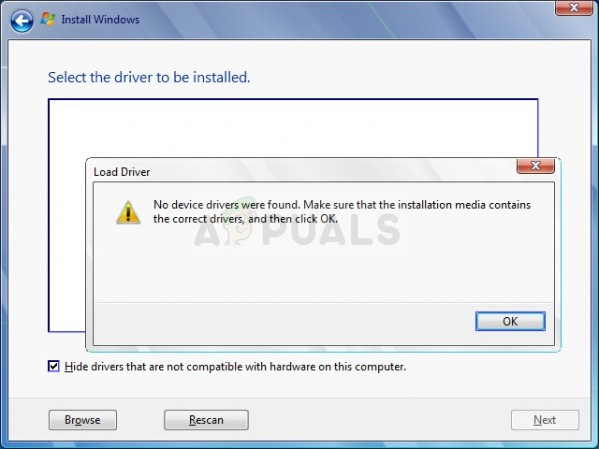
An administrator enables 1394 Kernel Debugging.
Someone who has physical access to the computer connects a 1394 storage device that complies with the SBP-2 specification.
1394 DMA threats to BitLocker
BitLocker system integrity checks mitigate unauthorized Kernel Debugging status changes. However, an attacker could connect an attacking device to a 1394 port, and then spoof an SBP-2 hardware ID. When Windows detects an SBP-2 hardware ID, it loads the SBP-2 driver (sbp2port.sys), and then instructs the driver to allow for the SBP-2 device to perform DMA. This enables an attacker to gain access to system memory and search for BitLocker encryption keys.
Thunderbolt physical DMA
Thunderbolt is an external bus that allows for direct access to system memory via PCI. This functionality is provided as a performance improvement. It enables large amounts of data to transfer directly between a Thunderbolt device and system memory, thereby bypassing the CPU and software.
Thunderbolt threats to BitLocker
An attacker could connect a special purpose device to a Thunderbolt port and have full direct memory access through the PCI Express bus. This could enable an attacker to gain access to system memory and search for BitLocker encryption keys. Note that Thunderbolt 3 on the new USB Type-C connector includes new security features which can be configured to protect against this type of access.
Resolution
Some configurations of BitLocker can reduce the risk of this kind of attack. The TPM+PIN, TPM+USB, and TPM+PIN+USB protectors reduce the effect of DMA attacks when computers do not use sleep mode (suspend to RAM).
SBP-2 Mitigation
On the previously mentioned website, refer to the 'Prevent installation of drivers matching these device setup classes' section under 'Group Policy Settings for Device Installation'.
The following is the Plug and Play device setup class GUID for an SBP-2 drive:
d48179be-ec20-11d1-b6b8-00c04fa372a7
On some platforms, completely disabling the 1394 device may provide extra security. On the previously mentioned website, refer to the 'Prevent installation of devices that match these device IDs' section under 'Group Policy Settings for Device Installation'.
The following is the Plug and Play compatible ID for a 1394 controller:
PCICC_0C0010
Thunderbolt Mitigation
Beginning with Windows 10 version 1803, newer Intel-based systems include built-in kernel DMA protection for Thunderbolt 3. No configuration is required for this protection.
To block a Thunderbolt controller on a device running an earlier version of Windows, or for platforms that lack kernel DMA protection for Thunderbolt 3, refer to the 'Prevent installation of devices that match these device IDs' section under 'Group Policy Settings for Device Installation' on the previously mentioned website.
Buffalo Port Devices Driver Updater
The following is the Plug and Play compatible ID for a Thunderbolt controller:
PCICC_0C0A
Notes
The drawback of this mitigation is that external storage devices can no longer connect by using the 1394 port, and all PCI Express devices that are connected to the Thunderbolt port will not work.
If your hardware deviates from current Windows Engineering Guidance, it may enable DMA on these ports after you start the computer and before Windows takes control of the hardware. This opens your system to compromise, and this condition is not mitigated by this workaround.
Blocking the SBP-2 driver and Thunderbolt controllers does not protect against attacks on external or internal PCI slots (including M.2, Cardbus & ExpressCard).
More Information
For more information about DMA threats to BitLocker, see the following Microsoft Security blog:
Windows BitLocker Claims For more information about mitigations for cold attacks against BitLocker, see the following Microsoft Integrity Team blog:
The third-party products that this article discusses are manufactured by companies that are independent of Microsoft. Microsoft makes no warranty, implied or otherwise, about the performance or reliability of these products.
-->Universal Serial Bus (USB) provides an expandable, hot-pluggable Plug and Play serial interface that ensures a standard, low-cost connection for peripheral devices such as keyboards, mice, joysticks, printers, scanners, storage devices, modems, and video conferencing cameras. Migration to USB is recommended for all peripheral devices that use legacy ports such as PS/2, serial, and parallel ports.
Buffalo Port Devices Drivers
The USB-IF is a Special Interest Groups (SIGs) that maintains the Official USB Specification, test specifications and tools.
Windows operating systems include native support for USB host controllers, hubs, and devices and systems that comply with the official USB specification. Windows also provides programming interfaces that you can use to develop device drivers and applications that communicate with a USB device.
Buffalo Port Devices Driver Ed
| USB in WindowsWindows 10: What's new for USB Overview of new features and improvements in USB in Windows 10. USB FAQFrequently asked questions from driver developers about the USB stack and features that are supported in USB. Microsoft OS Descriptors for USB DevicesWindows defines MS OS descriptors that allows better enumeration when connected to system running Windows operating system Microsoft-provided USB driversUSB device-side drivers in WindowsA set of drivers for handling common function logic for USB devices. USB host-side drivers in WindowsMicrosoft provides a core stack of drivers that interoperate with devices that are connected to EHCI and xHCI controllers. USB-IF device class driversWindows provides in-box device class drivers for many USB-IF approved device classes, audio, mass storage, and so on. USB generic function driver–WinUSBWindows provides Winusb.sys that can be loaded as a function driver for a custom device and a function of a composite device. USB generic parent driver for composite devices–UsbccgpParent driver for USB devices with multiple functions. Usbccgp creates physical device objects (PDOs) for each of those functions. Those individual PDOs are managed by their respective USB function drivers, which could be the Winusb.sys driver or a USB device class driver. WDF extension for developing USB drivers
Get information about the tools that you can use to test your USB hardware or software, capture traces of operations and other system events, and observe how the USB driver stack responds to a request sent by a client driver or an application. Read an overview of tests in the Hardware Certification Kit that enable hardware vendors and device manufacturers to prepare their USB devices and host controllers for Windows Hardware Certification submission. Other Resources for USB Official USB SpecificationProvides complete technical details for the USB protocol. Microsoft Windows USB Core Team BlogCheck out posts written by the Microsoft USB Team. The blog focuses on the Windows USB driver stack that works with various USB Host controllers and USB hubs found in Windows PC. A useful resource for USB client driver developers and USB hardware designers understand the driver stack implementation, resolve common issues, and explain how to use tools for gathering traces and log files. OSR Online Lists - ntdevDiscussion list managed by OSR Online for kernel-mode driver developers. Windows Dev-Center for Hardware DevelopmentMiscellaneous resources based on frequently asked questions from developers who are new to developing USB devices and drivers that work with Windows operating systems. USB-related videos UWP apps for USB devicesUnderstanding USB 3.0 in Windows 8Building great USB 3.0 devicesUSB Debugging Innovations in Windows 8 (Part I, II, & III)USB hardware for learning MUTT devicesMUTT and SuperMUTT devices and the accompanying software package are integrated into the HCK suite of USB tests. They provide automated testing that can be used during the development cycle of USB controllers, devices and systems, especially stress testing. OSR USB FX2 Learning KitIf you are new to USB driver development. The kit is the most suitable to study USB samples included in this documentation set. You can get the learning kit from OSR Online Store. | Write a USB client driver (KMDF, UMDF) Introduces you to USB driver development. Provides information about choosing the most appropriate model for providing a USB driver for your device. This section also includes tutorials about writing your first user-mode and kernel-mode USB drivers by using the USB templates included with Microsoft Visual Studio. Write a USB host controller driverIf you are developing an xHCI host controller that is not compliant with the specification or developing a custom non-xHCI hardware (such as a virtual host controller), you can write a host controller driver that communicates with UCX. For example, consider a wireless dock that supports USB devices. The PC communicates with USB devices through the wireless dock by using USB over TCP as a transport.
You can develop a controller driver that handles all USB data transfers and commands sent by the host to the device. This driver communicates with the Microsoft-provided USB function controller extension (UFX). USB function class extension (UFX) reference Write a USB Type-C connector driverWindows 10 introduces support for the new USB connector: USB Type-C. You can write a driver for the connector that communicates with the Microsoft-provided class extension module: UcmCx to handle scenarios related to Type-C connectors such as, which ports support Type-C, which ports support power delivery. USB connector manager class extension (UcmCx) reference Write a USB dual-role controller driverUSB Dual Role controllers are now supported in Windows 10. Windows includes in-box client drivers for ChipIdea and Synopsys controllers. For other controllers, Microsoft provides a set of programming interfaces that allow the dual-role class extension (UrsCx) and its client driver to communicate with each other to handle the role-switching capability of a dual-role controller. For more information about this feature, see: USB dual-role controller driver programming reference Write a USB driver for emulated devicesWindows 10 introduces support for emulated devices. Now you can develop an emulated Universal Serial Bus (USB) host controller driver and a connected virtual USB device. Both components are combined into a single KMDF driver that communicates with the Microsoft-provided USB device emulation class extension (UdeCx). Emulated USB host controller driver programming reference Write a UWP appProvides step-by-step instructions about implementing USB features in a UWP app. To write such an app for a USB device you need Visual Studio and Microsoft Windows Software Development Kit (SDK) . Write a Windows desktop appDescribes how an application can call WinUSB Functions to communicate with a USB device. WinUSB functions Common programming scenariosList of common tasks that a driver or an app performs in order to communicate with a USB device. Get quick info about the programming interfaces you need for each task. USB samples Development tools Download kits and tools for Windows |
